Safe systems of work help guard against crushing risk.
Entrapment is when one or more MEWP occupants become trapped between the controls, guardrails or other part of the MEWP and an immovable external object or structure.
Entrapment is consistently one of the top four causes of injuries
and fatalities when operating MEWPs.
- Contact with overhead obstructions in the path of the MEWP;
- leaning over the platform guardrails;
- losing control of the platform controls;
- lighting conditions making overhead obstructions difficult to see;
- operator becoming distracted while approaching
an overhead obstruction; - uneven ground causing vertical movements to the platform;
- objects on the ground in the path of the MEWP;
- operator overlooking risk to occupants in the platform,
IPAF has been collecting data on entrapment for more than 10
years. In the most recent 10-year period, there were a total of 127
reports from 17 countries and among those there were
108 fatalities
In the period 2020-22, there were 63 incidents involving
entrapment from 16 countries. There were 67 people involved
in entrapment incidents and there were 53 fatalities.
Analysis & outcomes
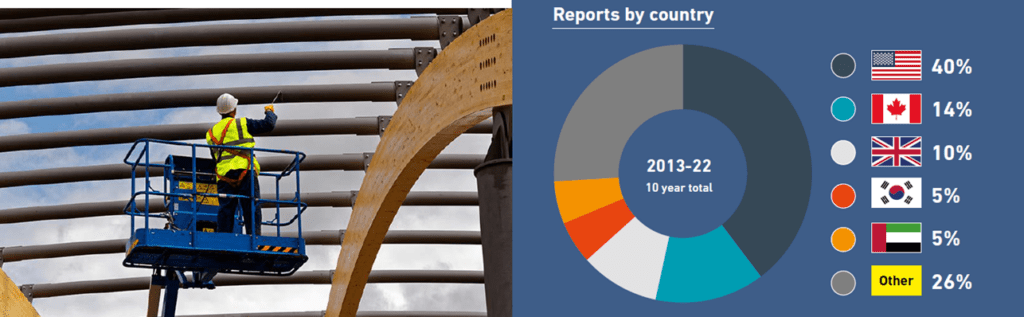
In 2022, IPAF received 18 reports of entrapment, up 29% on the previous year. Reports were received from nine countries, and there were 21 people involved, leading to 11 fatalities – down two compared to 2021 – meaning the rate of fatalities was down slightly year on year.
There were three reported entrapment fatalities in both Canada and Italy, representing 27% of the total worldwide. There was one fatality (9%) in the UK in 2022.
The majority of entrapment incidents occurred in construction, with 14 reports (78%), while facilities management saw two reports (11%) and arboriculture one (6%).
When broken down, construction suffered nine fatalities and four major injuries. Facilities management saw one death and one major injury, while arboriculture saw one fatality and no major injuries.
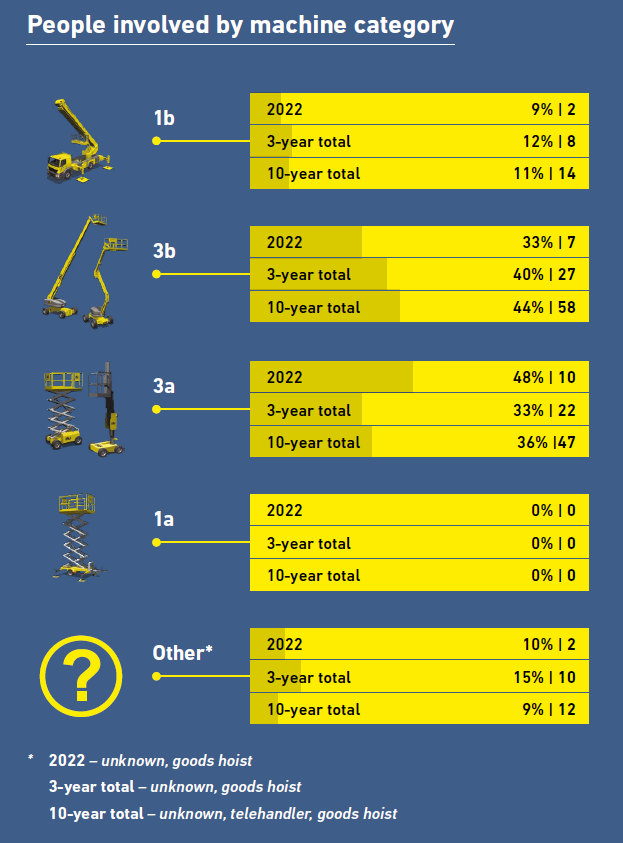
By machine type, 3b was the most common MEWP involved in entrapment incidents over the past 10 years, though just looking
at 2022 in isolation shows a spike in 3a machines, involved in 10 of the reports (48%). It remains to be seen whether this will be a long-term trend. Most entrapment incidents occurred in the elevated position, through two deaths occurred when MEWPs
were travelling in the lowered position.
MEWP operatives need to be aware of their surroundings whether travelling in the stowed position or driving/operating in the elevated position, as there is still potential for entrapment to occur. Operators should be aware that the risk of entrapment or
crushing can be increased in the stowed position, owing to higher drive speeds. Entrapment can be prevented by proper planning of MEWP operations and using MEWPs in a safe manner. Carrying out a thorough risk assessment and survey identifying potential entrapment areas at the workplace is crucial.